All Categories
Featured
Two individuals purchase joint annuities, which offer a surefire revenue stream for the rest of their lives. If an annuitant dies during the circulation period, the remaining funds in the annuity might be handed down to an assigned beneficiary. The particular options and tax obligation effects will rely on the annuity agreement terms and suitable regulations. When an annuitant dies, the passion gained on the annuity is taken care of in a different way depending upon the type of annuity. Most of the times, with a fixed-period or joint-survivor annuity, the interest remains to be paid to the making it through recipients. A death advantage is a function that makes certain a payment to the annuitant's beneficiary if they pass away before the annuity repayments are tired. Nevertheless, the schedule and terms of the fatality benefit may differ depending on the certain annuity agreement. A kind of annuity that stops all payments upon the annuitant's fatality is a life-only annuity. Recognizing the conditions of the survivor benefit prior to spending in a variable annuity. Annuities are subject to taxes upon the annuitant's death. The tax obligation treatment depends upon whether the annuity is kept in a qualified or non-qualified account. The funds undergo revenue tax in a certified account, such as a 401(k )or individual retirement account. Inheritance of a nonqualified annuity typically leads to taxation only on the gains, not the entire amount.

The original principal(the quantity originally transferred by the moms and dads )has currently been strained, so it's exempt to tax obligations once more upon inheritance. Nevertheless, the earnings portion of the annuity the passion or investment gains built up gradually is subject to revenue tax. Commonly, non-qualified annuities do.
have actually passed away, the annuity's benefits normally revert to the annuity proprietor's estate. An annuity proprietor is not legally required to notify existing beneficiaries regarding changes to recipient designations. The choice to alter recipients is typically at the annuity proprietor's discernment and can be made without alerting the current beneficiaries. Since an estate technically doesn't exist up until an individual has actually passed away, this beneficiary designation would only come right into result upon the death of the named person. Typically, once an annuity's owner dies, the marked beneficiary at the time of fatality is entitled to the advantages. The spouse can not transform the recipient after the owner's death, even if the recipient is a minor. Nevertheless, there might specify stipulations for taking care of the funds for a small beneficiary. This typically includes selecting a guardian or trustee to manage the funds up until the child reaches adulthood. Typically, no, as the recipients are exempt for your financial obligations. It is best to consult a tax specialist for a specific response related to your situation. You will remain to receive repayments according to the agreement timetable, however trying to get a swelling sum or loan is likely not an alternative. Yes, in virtually all situations, annuities can be acquired. The exemption is if an annuity is structured with a life-only payment alternative via annuitization. This sort of payment ceases upon the death of the annuitant and does not give any type of recurring worth to heirs. Yes, life insurance coverage annuities are normally taxed
When taken out, the annuity's profits are taxed as normal earnings. Nonetheless, the primary quantity (the first financial investment)is not exhausted. If a beneficiary is not called for annuity advantages, the annuity proceeds typically go to the annuitant's estate. The circulation will comply with the probate procedure, which can delay payments and might have tax obligation ramifications. Yes, you can call a trust as the recipient of an annuity.
Inherited Flexible Premium Annuities taxation rules
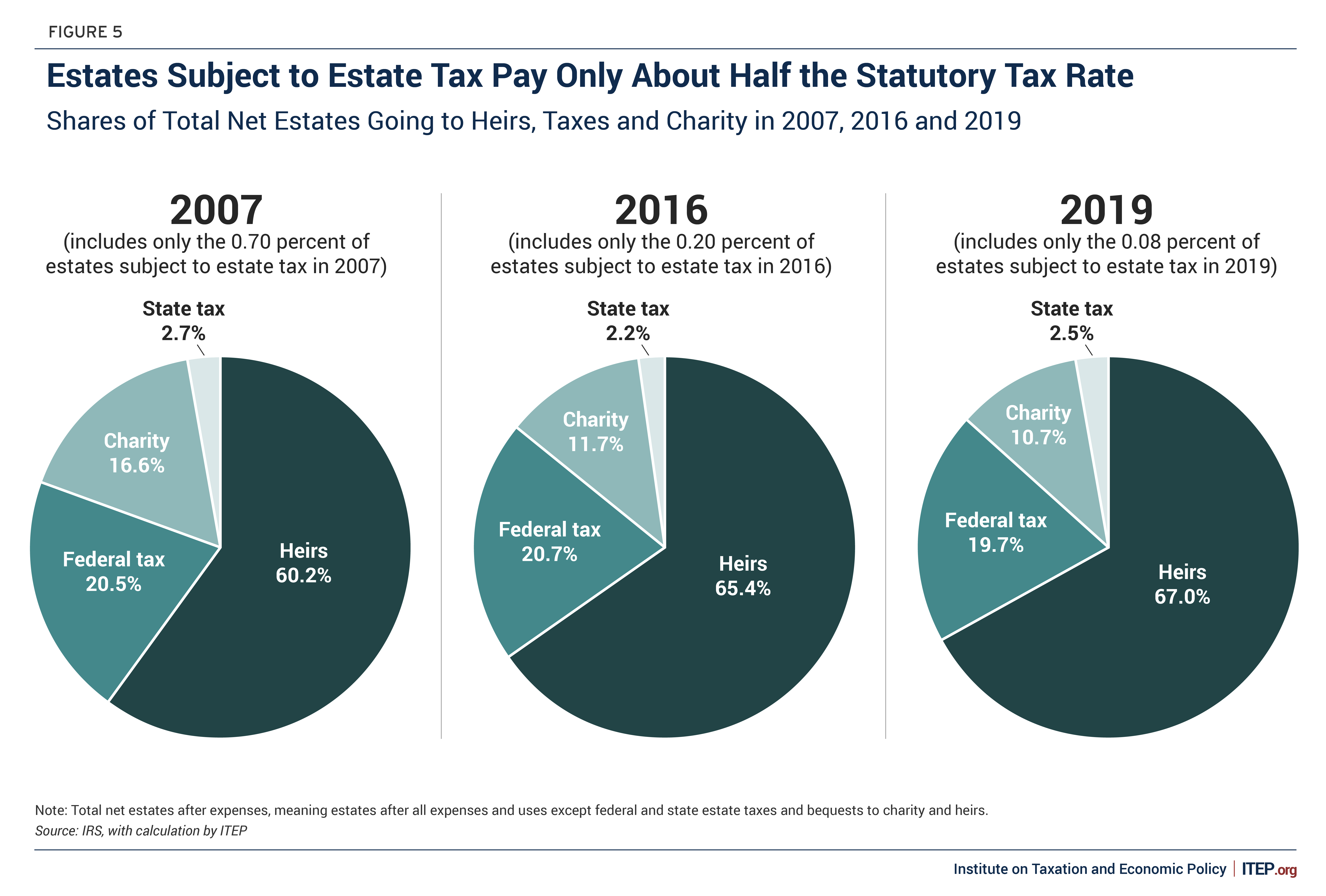
Whatever part of the annuity's principal was not currently exhausted and any kind of revenues the annuity built up are taxable as revenue for the beneficiary. If you acquire a non-qualified annuity, you will only owe tax obligations on the earnings of the annuity, not the principal used to buy it. Due to the fact that you're getting the whole annuity at once, you must pay tax obligations on the entire annuity in that tax obligation year.
Latest Posts
Understanding Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Indexed Annuity A Closer Look at Annuities Fixed Vs Variable What Is the Best Retirement Option? Pros and Cons of Variable Annuities Vs Fixed Annuities Why Vari
Understanding Financial Strategies Key Insights on Immediate Fixed Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Breaking Down the Basics of Investment Plans Advantages and Disadvantages of Immediate Fixed Annuity Vs V
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments Everything You Need to Know About Fixed Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Breaking Down the Basics of Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Benefits
More
Latest Posts